Land management software enables organizations to digitally record, monitor, and manage land-related data such as ownership details, zoning information, land use, and spatial boundaries from a centralized system.
It replaces fragmented manual processes with structured, data-driven workflows, improving accuracy and operational efficiency.
With increasing urbanization, infrastructure expansion, and regulatory complexity, the demand for digital land systems is growing rapidly. Governments, real estate developers, agricultural enterprises, and utility providers are adopting modern solutions to ensure transparency, compliance, and faster decision-making.
As a result, land development software is becoming a critical tool for managing land assets efficiently while supporting long-term planning and sustainable development.
What Is Land Management Software?
Types of Land Management Software
1. Agricultural Land Management
Agricultural land management software is designed to manage farmland boundaries, soil data, crop planning, and land utilization. These systems help agricultural enterprises monitor productivity, optimize resource usage, and plan cultivation cycles efficiently.
Modern land management software solutions in agriculture often integrate GIS mapping and historical land data to support sustainable farming and long-term land optimization.
2. Real Estate & Property Management
Real estate and property management platforms enable developers and landowners to track land parcels, ownership details, zoning regulations, and development timelines.
Often used as land development project management software, these systems streamline land acquisition, documentation, approvals, and project coordination while improving visibility across multiple development initiatives.
3. Government Land Records Systems
Government land records systems focus on digitizing and maintaining public land data, ownership records, and legal documentation.
Implemented as land records management software, these platforms enhance transparency, reduce land disputes, and ensure regulatory compliance by providing secure, role-based access to authorized departments and stakeholders.
4. Infrastructure & Utility Land Management
Infrastructure and utility land management software supports projects such as highways, pipelines, power grids, and telecommunications networks.
These platforms are typically deployed as large-scale enterprise solutions, helping organizations manage right-of-way data, land acquisition processes, asset placement, and regulatory approvals across geographically dispersed projects.
Core Features of Land Management Software
1. GIS-Based Land Parcel Mapping
GIS-based land parcel mapping enables accurate visualization of land boundaries, plots, and spatial data on interactive maps.
It allows users to analyze land location, area, and usage patterns while integrating satellite imagery and geospatial layers for better planning and decision-making.
2. Ownership & Document Management
This feature centralizes ownership records, title details, and legal documents in a secure digital repository. It ensures easy access to historical data, reduces paperwork, and helps maintain accurate, up-to-date land ownership information.
3. Zoning & Compliance Tracking
Zoning and compliance tracking helps organizations monitor land-use regulations, zoning classifications, and statutory requirements. Automated alerts and validation mechanisms reduce the risk of non-compliance and support smoother approvals and audits.
4. Lease & Contract Management
Lease and contract management enables tracking of land leases, agreements, renewal dates, and payment schedules. It improves contract visibility, minimizes missed deadlines, and supports better financial and legal control over land assets.
5. Workflow Automation & Reporting
Workflow automation streamlines approvals, task assignments, and operational processes across departments. Built-in reporting and analytics provide insights into land utilization, project progress, and compliance status through customizable dashboards.
6. Mobile and Role-Based Access
It ensures secure system usage for different stakeholders based on their roles and permissions. Mobile accessibility allows field teams to collect, update, and access land data in real time, even from remote locations.
Benefits of Land Management Software
- Centralized land data: Consolidates land parcels, ownership records, zoning details, and documents into a single platform, enabling organizations to manage 100% of land data from one system.
- Improved accuracy and transparency: Automated data validation and audit trails reduce manual errors and disputes, with digital systems improving land record accuracy by 30–40% compared to paper-based processes.
- Faster decision-making: Real-time dashboards and GIS insights help stakeholders evaluate land status quickly, cutting approval and verification timelines by 40–50%.
- Reduced operational costs: Automation and reduced paperwork can lower administrative and operational expenses by 20–30% over time.
- Better regulatory compliance: Built-in zoning and compliance tracking reduces the risk of violations, helping organizations achieve up to 25% fewer compliance-related issues.
- Enhanced productivity: Workflow automation minimizes repetitive tasks, allowing teams to handle 30–45% more land records with the same workforce.
- Scalability for large land portfolios: Supports management of thousands of land parcels across multiple locations without proportional increases in cost or manpower.
- Improved stakeholder collaboration: Shared access and role-based permissions improve coordination across departments, reducing information delays by up to 35%.
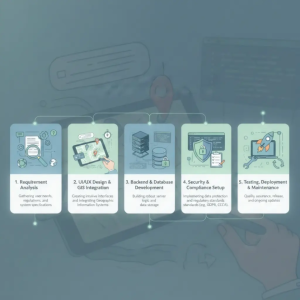
Steps to Develop Land Management Software Development
| Development Step | Scope of Work | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Requirement Analysis | Stakeholder consultation, use-case definition, feature planning, technical documentation | $3,000 – $7,000 |
| UI/UX Design & GIS Integration | Dashboard design, map-based UI, GIS tools integration (Mapbox, Google Maps, ArcGIS) | $6,000 – $15,000 |
| Backend & Database Development | API development, business logic, spatial database setup (PostgreSQL + PostGIS), integrations | $12,000 – $30,000 |
| Security & Compliance Setup | Role-based access, data encryption, audit logs, regulatory compliance | $4,000 – $10,000 |
| Testing, Deployment & Maintenance | Functional testing, GIS accuracy testing, cloud deployment, ongoing support | $5,000 – $12,000 |
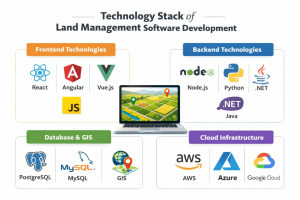
Technology Stack of Land Management Software Development
1. Frontend Technologies
The frontend of land management software is typically developed using modern frameworks such as React or Angular.
These frameworks enable responsive, interactive user interfaces and map-driven dashboards, supporting real-time data visualization and smooth user interactions with complex land and spatial data.
2. Backend Technologies
On the backend, Node.js and Python are commonly used to handle application logic, API development, data processing, and integration with external systems.
These technologies provide scalability and high performance, essential for managing large volumes of land records and GIS operations efficiently.
4. Database & GIS
PostgreSQL combined with PostGIS is widely used for storing structured land records and handling geospatial data.
This setup supports advanced geolocation queries, land parcel mapping, boundary analysis, and integration with GIS tools, ensuring accurate spatial data management.
5. Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are used for deployment and scaling. They provide high availability, secure data storage, backup, and performance optimization, ensuring the system can handle increasing data volume and user demands effectively.
Development Cost & Timeline of Landing Software Development
1. MVP vs Full-Scale System
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) of land management software typically focuses on core features such as land parcel mapping, ownership records, and basic compliance tracking, with software development cost varying based on complexity and features.
The estimated cost for an MVP ranges from $30,000 to $45,000, with a development timeline of 3–5 months depending on complexity and GIS integrations.
A full-scale system, including advanced features like lease and contract management, workflow automation, reporting dashboards, mobile access, and enterprise-level security, can cost between $50,000 and $80,000+.
The development timeline for a full-scale solution is generally 6–9 months, factoring in extensive testing, multi-user support, and integration with third-party GIS and government databases.
Key Cost Factors
- Feature Scope: The number of modules and functionalities directly impacts development cost. Advanced features like automated workflows and analytics dashboards increase both cost and timeline.
- GIS Integration: Integrating satellite data, mapping tools, and spatial analytics can add $5,000–$15,000 depending on complexity.
- Database & Infrastructure: Spatial databases (PostGIS/PostgreSQL) and cloud infrastructure setup can cost $8,000–$12,000, depending on scalability and redundancy needs.
- Security & Compliance: Implementing role-based access, encryption, and regulatory compliance may add $4,000–$10,000.
- Maintenance & Support: Ongoing maintenance, updates, and cloud hosting typically cost 10–15% of the initial development cost annually.
Use Cases by Industry
1. Government Land Registries
Land management software is widely used by government agencies to digitize and maintain public land records. It helps streamline ownership tracking, manage cadastral maps, and ensure transparency in land transactions.
By implementing land records management software, governments can reduce disputes, improve regulatory compliance, and provide citizens with easy access to verified land data.
2. Smart City Planning
In smart city initiatives, land management software supports urban planning, zoning compliance, and infrastructure development.
Planners can analyze land use, monitor development projects, and optimize public spaces. These systems enable data-driven decisions for sustainable growth and efficient allocation of land resources.
3. Agriculture and Farm Management
Agricultural enterprises and farm owners use land management software to track field boundaries, soil data, irrigation schedules, and crop rotation plans. With land management software solutions, farmers can increase productivity, monitor land utilization, and implement sustainable practices while reducing operational inefficiencies.
4. Commercial Real Estate
Real estate developers and property managers rely on land management software for tracking land parcels, managing leases, and monitoring development progress.
Land development project management software helps streamline acquisitions, ensure regulatory compliance, and improve project visibility across multiple sites, making large-scale real estate development more efficient and transparent.
Challenges & Solutions of Land Management Software Development
1. Data Inconsistency
Challenge: Manual record-keeping and fragmented systems often lead to errors, missing information, and inconsistent land data, making decision-making difficult.
Solution: Implementing a centralized land management software ensures all data is stored in a single repository with validation checks, reducing errors and improving accuracy by up to 30–40%.
2. GIS Performance
Challenge: Handling large geospatial datasets and complex mapping operations can slow down the system and affect real-time analysis.
Solution: Using optimized spatial databases like PostGIS, caching techniques, and cloud-based GIS services ensures smooth performance and fast map rendering, even for large-scale land portfolios.
3. Legal Compliance
Challenge: Land regulations, zoning laws, and documentation requirements vary across regions, making compliance complex.
Solution: Built-in compliance modules, automated alerts, and workflow tracking in land management software help ensure adherence to local laws and reduce risks of violations.
4. User Adoption
Challenge: Resistance from staff accustomed to traditional manual processes can delay implementation.
Solution: Intuitive UI/UX design, mobile access, role-based permissions, and training programs make it easier for users to adapt, improving adoption rates and operational efficiency.
Future Trends of Land Management Software Development
1. AI-Driven Land Analytics
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing land management by providing predictive insights, optimizing land use, and improving decision-making.
AI can analyze historical land records, ownership patterns, environmental factors, and market trends to forecast land value, detect risks, and support strategic development.
2. Drone & Satellite Integration
Integration of drones and satellite imagery allows real-time land surveying, boundary verification, crop monitoring, and environmental assessments. High-resolution geospatial data improves accuracy, reduces manual fieldwork, and enables proactive land management.
3. Blockchain-Based Land Records
Blockchain creates secure, tamper-proof digital ledgers of ownership and transaction history, reducing fraud and enhancing transparency.
Governments and enterprises can streamline property transfers while maintaining an immutable record of land transactions.
4. IoT-Enabled Land Monitoring
Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as soil sensors and smart irrigation systems, enable continuous monitoring of land conditions.
This real-time data helps farmers, municipalities, and infrastructure planners optimize resource usage, detect anomalies, and improve land sustainability.
5. Cloud-Based Collaborative Platforms
Cloud platforms allow multiple stakeholders—government agencies, developers, surveyors, and farmers—to access, update, and collaborate on land data in real time.
Cloud-based systems enhance scalability, data security, and remote accessibility, especially for large or distributed land portfolios.
6. Augmented Reality (AR) & 3D Mapping
AR and 3D mapping technologies provide immersive visualization of land parcels, proposed developments, and terrain features.
This helps urban planners, architects, and developers make better planning decisions and communicate project layouts more effectively to stakeholders.
7. Predictive Environmental Impact Analysis
Advanced software can simulate the environmental impact of land development projects, such as soil erosion, water usage, and deforestation. Predictive modeling enables sustainable planning and compliance with environmental regulations.
These emerging trends indicate that the future of land management software will increasingly rely on automation, advanced analytics, and integrated technologies to make land administration smarter, faster, and more transparent.
Why Choose AleaIT Solutions for Land Management Software Development
Our solutions are secure and scalable, capable of handling large datasets, complex workflows, and multiple users, with cloud deployment, role-based access, and data encryption to protect sensitive information.
We provide end-to-end development support, covering requirement analysis, UI/UX design, backend development, GIS integration, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance, ensuring timely delivery, high performance, and maximum ROI.
This combination of technical expertise, security, scalability, and full lifecycle support makes AleaIT Solutions a trusted partner for modern land management solutions.
FAQs
Q1. How long does it take to develop land management software and what is the cost?
An MVP with core features typically takes 3–5 months and costs $30,000–$45,000, while a full-scale system with advanced modules like workflow automation, mobile access, and reporting dashboards may take 6–9 months and cost $50,000–$80,000+ depending on complexity.
Q2. Which GIS tools are best for land management software?
Common GIS tools include PostGIS for spatial database management, ArcGIS for advanced mapping and analytics, Mapbox for interactive maps, and Google Maps API for location services. The choice depends on project requirements, data volume, and budget.
Q3. Can land management software integrate with other systems?
Yes, it can integrate with government land records, ERP systems, IoT devices, and satellite data sources. API-based integration ensures real-time updates, interoperability, and seamless data flow across platforms.
Q4. What industries benefit most from land management software?
Industries such as government agencies, real estate, agriculture, utilities, and environmental management benefit the most. It helps these sectors manage land records efficiently, ensure compliance, and improve operational decision-making.
Q5. Is mobile access available in land management software?
Yes, most modern agriculture solutions offer mobile access for field teams, allowing users to update land records, verify boundaries, and collect data remotely, even offline, ensuring real-time synchronization when back online.
Q6. Can AI and analytics be integrated into land management software?
Absolutely. AI-driven analytics can forecast land value, detect anomalies in ownership data, optimize land use, and provide predictive insights for strategic planning, making the system smarter over time.
Q7. What are the security features of land management software?
Modern software includes role-based access, data encryption, secure cloud storage, and audit logs, protecting sensitive land information from unauthorized access and ensuring regulatory compliance.